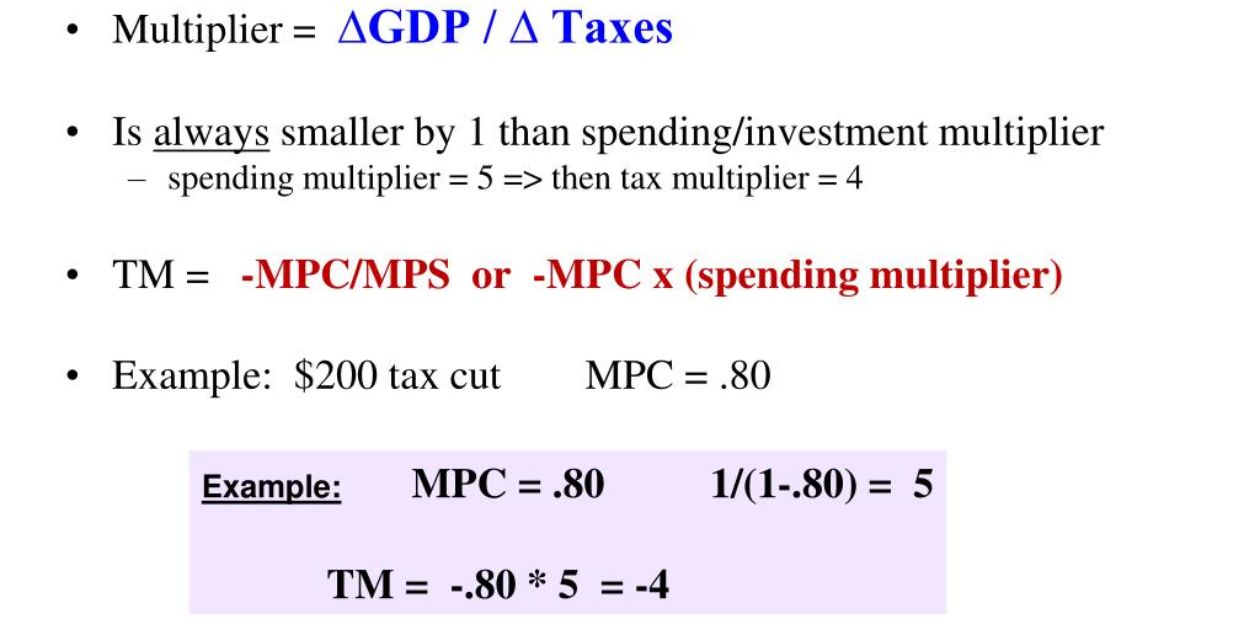
In a world where data reigns supreme, understanding how to extract valuable insights from tables is a skill that sets professionals apart. Today, we delve into the art of locating the Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) from a table. By dissecting the relationship between income and consumption, we will unravel the factors influencing MPC and equip you with the practical knowledge to calculate it. Join us on this analytical journey as we navigate the depths of table data to uncover the secrets of MPC.
Key Takeaways
• MPC represents the proportion of additional income spent rather than saved
• Analyzing tables helps determine the relationship between income and spending patterns
• Understanding MPC is crucial for predicting changes in expenditure
• Extracting insights from tables enhances knowledge of consumer behavior
Step-by-Step Guide to Locating MPC in a Table
The first step in locating the MPC in a table is to carefully examine the rows and columns for the desired data point. The MPC, or marginal propensity to consume, represents the proportion of additional income that individuals choose to spend rather than save. By analyzing the data provided in the table, one can determine the relationship between income and spending patterns. As income increases, the level of consumption also tends to rise, indicating a higher MPC. This indicates that individuals are more inclined to spend a larger portion of their income. Understanding the MPC is crucial in predicting changes in expenditure as it helps determine how much money people are likely to spend when their level of income changes. By examining the table closely, one can identify the specific values that represent the MPC and gain valuable insights into consumer behavior.
Understanding the Relationship Between Income and Consumption
In order to fully comprehend the relationship between income and consumption, it is essential to analyze the data and identify patterns that indicate the extent to which individuals allocate their income towards spending. By examining income levels and consumption behavior, we can gain valuable insights into the factors that influence spending decisions.
To understand this relationship, it is important to consider the concept of the consumption function. This function represents the relationship between aggregate income and household consumption. It takes into account factors such as disposable income, propensity to spend, and autonomous consumption.
Key factors that influence the relationship between income and consumption include the level of disposable income, which refers to the income available for spending after taxes and other deductions. Additionally, the propensity to spend plays a crucial role in determining how much of their income individuals allocate towards consumption.
Understanding the relationship between income and consumption is important for policymakers and economists, as it helps them forecast future spending patterns and make informed decisions about economic policies. By analyzing data on household income and consumption, we can gain a deeper understanding of the average propensity to consume and how it impacts overall economic growth.
Analyzing Data to Determine Marginal Propensity to Consume
By examining the data, we can analyze the spending patterns and identify the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), providing valuable insights for policymakers and economists. One method of analyzing data to determine the MPC is by using a table. The table presents different levels of income and the corresponding levels of consumption. By comparing the changes in income and consumption, we can calculate the MPC. The MPC represents the proportion of additional income that is spent on consumption. To find the MPC from a table, we need to calculate the change in consumption and the change in income for each level. The MPC is then determined by dividing the change in consumption by the change in income. This analysis is relevant and contextually important in understanding the consumption function and making informed policy decisions.
Key Factors Influencing MPC in Table Data
Several key factors, such as income levels and consumption patterns, significantly influence the MPC in table data. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) represents the proportion of an increase in income that is spent on consumption. It is an important economic indicator that helps analyze the relationship between income and spending. The following are two sub-lists that highlight the key factors influencing the MPC in table data:
Factors influencing MPC: – Income levels: – An increase in income generally leads to an increase in spending. Higher income allows individuals to have more disposable income, which in turn stimulates consumption. – Consumption increases when income taxes are reduced, as individuals have more money available to spend.
• Consumption patterns:
• Changes in consumer preferences and tastes can influence the MPC. For example, if there is a shift towards more luxurious goods, the MPC may increase as individuals spend a larger proportion of their income on these goods.
• Exports also play a role in influencing the MPC. An increase in exports leads to an increase in income, which can in turn lead to an increase in spending.
Practical Application: Using Table Data to Calculate MPC

To calculate the MPC, economists can utilize table data and employ mathematical formulas. The MPC, or marginal propensity to consume, measures the change in consumption that occurs in response to a change in income. It is calculated by dividing the change in consumption by the change in income. By examining table data that shows the relationship between income and consumption, economists can determine the MPC by comparing the changes in these variables. This information is crucial for understanding consumer behavior and predicting the impact of income changes on consumer spending. Additionally, the MPC is an important component in calculations related to aggregate output, such as the expenditure multiplier. By analyzing the income elasticity of consumer spending and the income after tax, economists can further refine their understanding of autonomous consumer spending and its impact on the overall economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Determine the Average Propensity to Consume (Apc) From the Table Data?
To determine the average propensity to consume (APC) from table data, analyze the consumption expenditures over different income levels and calculate the ratio of consumption to income. This provides insights into consumer behavior and spending patterns.
What Are Some Limitations of Using Table Data to Calculate the Marginal Propensity to Consume (Mpc)?
Some limitations of using table data to calculate the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) include potential inaccuracies due to data collection methods, assumptions made in constructing the table, and the inability to capture all relevant factors influencing consumption behavior.
Are There Any Alternative Methods to Determine the MPC if Table Data Is Not Available?
Alternative methods to determine the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) when table data is unavailable include regression analysis, econometric models, and time series analysis. These methods provide a data-driven approach to estimating the MPC.
How Does the Concept of Disposable Income Relate to the Marginal Propensity to Consume?
The concept of disposable income is crucial in understanding the relationship with the marginal propensity to consume (MPC). Disposable income represents the portion of income available for spending, and the MPC measures the proportion of that income that is consumed.
Can Changes in Government Policies or Regulations Affect the MPC Values Observed in the Table Data?
Changes in government policies or regulations can potentially impact the observed values of the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) in the table data. These changes can affect factors such as disposable income, consumer behavior, and overall economic conditions, leading to variations in MPC.
Conclusion
In conclusion, locating the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) in a table requires a step-by-step analysis of the data and understanding the relationship between income and consumption. By analyzing the data and considering key factors influencing the MPC, one can accurately determine the level of consumption that changes in income will cause. This information is valuable for predicting consumer behavior and making informed economic decisions. For example, a study may find that an increase in income by 10% leads to a 5% increase in consumption, indicating an MPC of 0.5.

Brook over 3 years of professional gaming, esports coaching, and gaming hardware reviews to provide insightful expertise across PC, console, and mobile gaming.