In the dynamic realm of economics, understanding the multiplier effect and how to calculate it from the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the multiplier from MPC, exploring its impact on the economy and shedding light on different types of multipliers. With a concise and analytical approach, we navigate through the data-driven world of economics, offering insights that will empower you to make informed decisions and foster a sense of belonging in the field.
Key Takeaways
• The multiplier effect is a concept in economics that explains how an initial increase in spending leads to a larger overall increase in economic activity.
• The multiplier effect is driven by the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), which is the proportion of additional income that individuals choose to spend rather than save.
• The Keynesian Multiplier is calculated using the formula MPC / (1 – MPC) and indicates the overall impact of an increase in government spending on national income.
• The money supply multiplier measures the increase in the supply of money resulting from an initial injection of funds into the banking system and is determined by the MPC.
The Multiplier Effect Explained
The Multiplier Effect, which is a concept widely used in economics, can be explained as the phenomenon in which an initial increase in spending leads to a larger overall increase in economic activity. This concept is based on the idea that when individuals or businesses spend money, it creates income for others, who in turn spend a portion of that income, creating even more income for others. The multiplier effect is driven by the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), which is the proportion of additional income that individuals choose to spend rather than save. The higher the MPC, the larger the multiplier effect. Understanding the multiplier effect is crucial for policymakers and economists as it helps them predict the impact of changes in spending on the overall economy. By quantifying the multiplier effect through the spending multiplier, policymakers can make informed decisions to stimulate economic growth and stability.
Calculating the Keynesian Multiplier
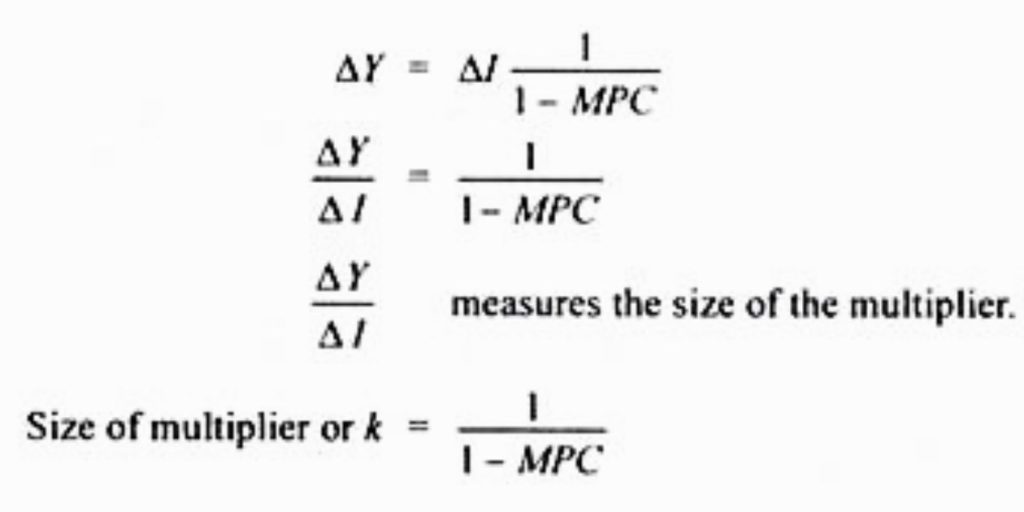
Since the Keynesian Multiplier is an important tool for understanding the impact of changes in government spending on the overall economy, it is crucial to accurately calculate it using the formula MPC / (1 – MPC). The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the factor that determines how much money individuals will spend out of an increase in income. It represents the ratio of the increase in spending to the increase in income. By dividing the MPC by 1 minus the MPC, we can calculate the multiplier, which indicates the overall impact of an increase in government spending on national income. For example, if the MPC is 0.8, the multiplier would be 5 (0.8 / (1 – 0.8) = 5). This means that for every initial spending of $1 by the government, the national income would increase by $5. The multiplier is a crucial factor in understanding the potential impact of government expenditure on the economy.
Understanding the Money Supply Multiplier
Our understanding of the money supply multiplier and its implications for the economy can be enhanced by analyzing the relationship between changes in the money supply and changes in aggregate demand. The money supply multiplier, also known as the reserve multiplier, measures the increase in the supply of money that results from an initial injection of funds into the banking system. This multiplier effect occurs because banks are required to hold only a fraction of their deposits as reserves, allowing them to lend out the remaining funds. The multiplier is determined by the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), which represents the proportion of additional income that is spent rather than saved. Understanding the money supply multiplier is essential for policymakers and economists as it provides insights into how changes in the money supply can impact aggregate demand and, consequently, the overall health of the economy.
To evoke an emotional response in the audience, consider the following:
1. The money supply multiplier demonstrates the power of monetary policy in stimulating economic growth and creating jobs.
2. Understanding the multiplier effect allows individuals to grasp the interconnectedness of the financial system and the real economy.
3. Changes in the money supply can have a significant impact on inflation and interest rates, affecting the purchasing power and financial well-being of individuals and businesses.
4. By comprehending the money supply multiplier, individuals can have a more informed voice in economic discussions and contribute to shaping policies that promote stability and prosperity.
Different Types of Multipliers
Through an analysis of various economic models, we can gain a deeper understanding of the distinct mechanisms and impacts associated with different types of multipliers. One commonly discussed multiplier is the expenditure multiplier, which measures the change in aggregate demand resulting from a change in spending. It is determined by the consumption function, which relates consumer spending to income. Another important multiplier is the investment multiplier, which measures the impact of an increase in investment on income and economic activity. When income increases due to investment, it leads to a further increase in aggregate demand, resulting in multiplier effects. Similarly, when government spending increases, it stimulates economic activity through the multiplier effect, as additional spending by consumers drives up aggregate demand. Understanding these different types of multipliers is crucial in analyzing the impact of spending increases and government policies on the economy.
Impact of the Multiplier Effect

The multiplier effect has a significant impact on the economy, as it amplifies the initial change in spending and leads to a larger overall increase in aggregate demand. This phenomenon occurs due to the consumption behavior of individuals, known as the marginal propensity to consume (MPC). Here are four ways in which the multiplier effect affects the economy:
1. Boosts economic growth: The multiplier effect helps stimulate economic growth by creating a chain reaction of increased spending and production.
2. Increases employment: As aggregate demand rises, businesses expand their operations to meet the increased demand, leading to job creation and reduced unemployment rates.
3. Supports government spending: The multiplier effect allows governments to use fiscal policies, such as increased infrastructure spending, to stimulate the economy and support various sectors.
4. Enhances business investment: The multiplier effect encourages businesses to invest in new projects and expand their operations, which further boosts economic activity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Multiplier Effect Impact Government Spending and Taxation Policies?
The multiplier effect has significant implications for government spending and taxation policies. It magnifies the impact of changes in these policies on the overall economy, stimulating or dampening economic activity and influencing GDP growth and employment levels.
Can the Multiplier Effect Be Used to Measure the Impact of Changes in Investment Levels?
The multiplier effect can be used to measure the impact of changes in investment levels. By calculating the multiplier, which represents the change in output resulting from a change in investment, policymakers can assess the potential economic growth stimulated by different investment levels.
What Are Some Factors That Can Influence the Size of the Multiplier Effect?
Factors that can influence the size of the multiplier effect include the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), the level of investment, the presence of leakages or injections in the economy, and the overall state of aggregate demand.
Is the Multiplier Effect Applicable to Both Closed and Open Economies?
The multiplier effect applies to both closed and open economies. It is a concept that measures the impact of an initial change in spending on overall economic output, taking into account the subsequent rounds of spending and income generation.
How Does the Multiplier Effect Differ Between Short-Run and Long-Run Economic Scenarios?
The multiplier effect differs between short-run and long-run economic scenarios based on the time frame and factors affecting aggregate demand. In the short run, the multiplier effect may be higher due to sticky wages and prices, while in the long run, it may be lower due to adjustments in wages and prices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the multiplier effect is a powerful economic concept that shows how changes in spending can have a multiplied impact on the overall economy. By understanding and calculating different types of multipliers, policymakers and economists can better predict the effects of fiscal and monetary policies. The multiplier effect is like a ripple in a pond, spreading economic activity and creating a chain reaction of growth and prosperity. It is a crucial tool in analyzing and shaping economic outcomes.

Brook over 3 years of professional gaming, esports coaching, and gaming hardware reviews to provide insightful expertise across PC, console, and mobile gaming.










